Chromophoric dissolved organic matter in inland waters: Present knowledge and future challenges
New publication by Yunlin Zhang, Lei Zhou, Yongqiang Zhou, Liuqing Zhang, Xiaolong Yao, Kun Shi, Erik Jeppesen, Qian Yu, Weining Zhu
Abstract
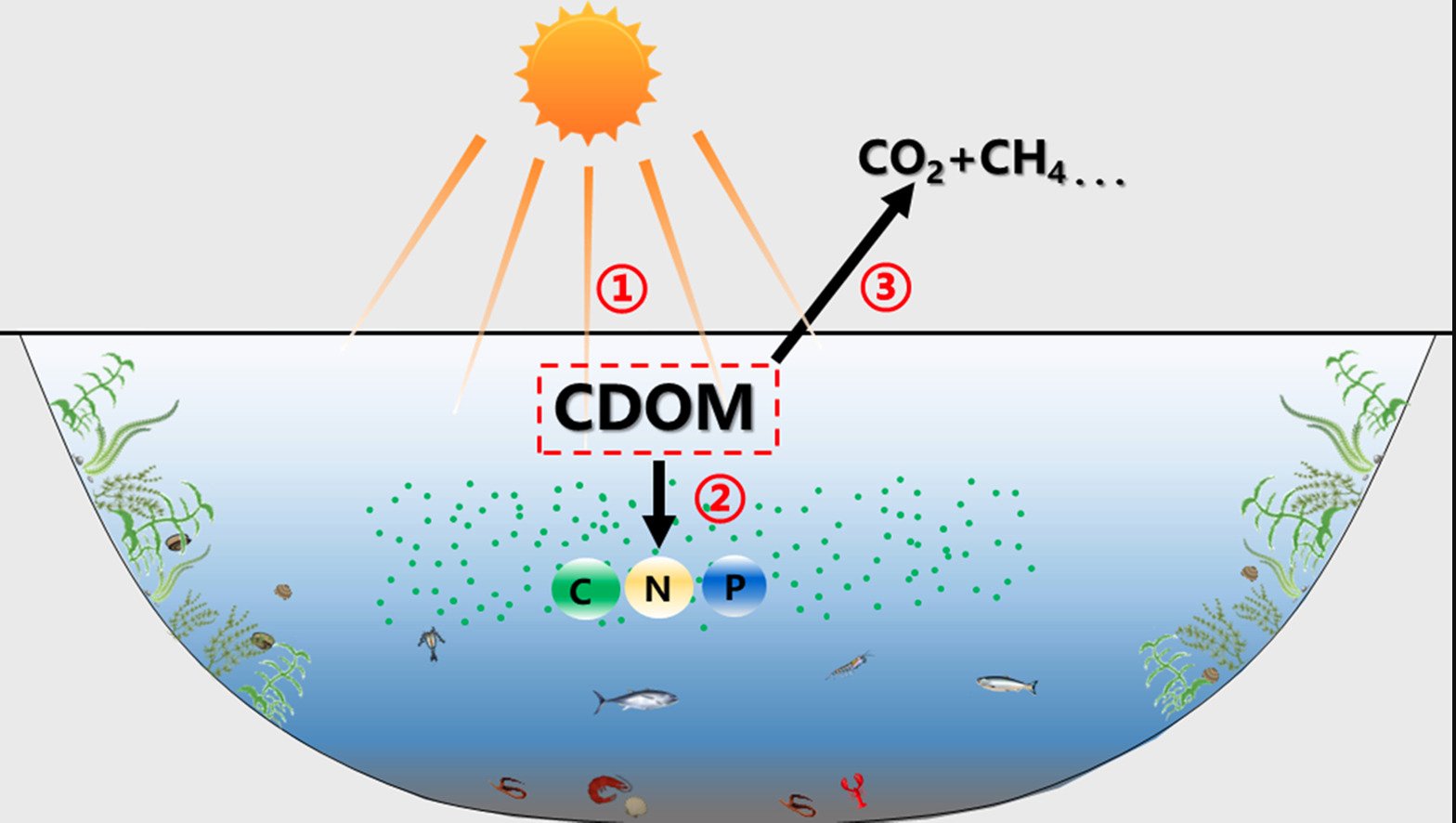
Chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) plays an important role in the biogeochemical cycle and energy flow of aquatic ecosystems. Thus, systematic and comprehensive understanding of CDOM dynamics is critically important for aquatic ecosystem management. CDOM spans multiple study fields, including analytical chemistry, biogeochemistry, water color remote sensing, and global environmental change. Here, we thoroughly summarize the progresses of recent studies focusing on the characterization, distribution, sources, composition, and fate of CDOM in inland waters. Characterization methods, remote sensing estimation, and biogeochemistry cycle processes were the hotspots of CDOM studies. Specifically, optical, isotope, and mass spectrometric techniques have been widely used to characterize CDOM abundance, composition, and sources. Remote sensing is an effective tool to map CDOM distribution with high temporal and spatial resolutions. CDOM dynamics are mainly determined by watershed-related processes, including rainfall discharge, groundwater, wastewater discharges/effluents, and biogeochemical cycling occurring in soil and water bodies. We highlight the underlying mechanisms of the photochemical degradation and microbial decomposition of CDOM, and emphasize that photochemical and microbial processes of CDOM in inland waters accelerate nutrient cycling and regeneration in the water column and also exacerbate global warming by releasing greenhouse gases. Future study directions to improve the understanding of CDOM dynamics in inland waters are proposed. This review provides an interdisciplinary view and new insights on CDOM dynamics in inland waters.
