Co-processing plastics waste and biomass by pyrolysis–gasification: a review
New publication by Peter Nai Yuh Yek, Yi Herng Chan, Shin Ying Foong, Wan Adibah Wan Mahari, Xiangmeng Chen, Rock Keey Liew, Nyuk Ling Ma, Yiu Fai Tsang, Christian Sonne, Yoke Wang Cheng, Yie Hua Tan, Su Shiung Lam.
Abstract:
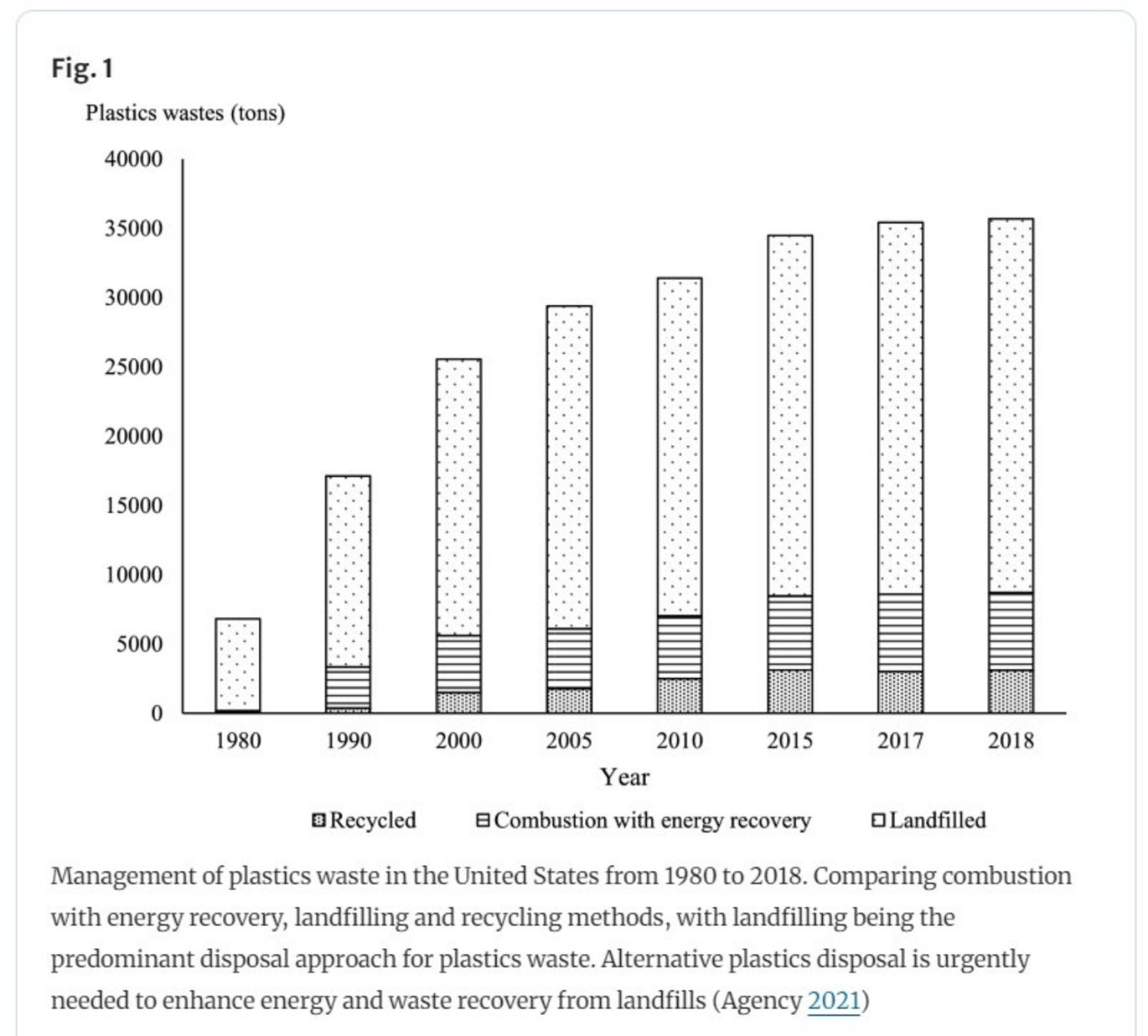
Escalating global population and expanding industrialisation have significantly contributed to an increased demand for plastics. Methods for plastic waste disposal predominantly involve landfilling, which consumes space and pollutes soil and water bodies, posing a substantial threat to the environment and public health. The critical challenge herein lies in efficiently managing the abundant biomass and plastics waste. Here we review gasification and pyrolysis, two prominent waste treatment processes. Co-pyrolysis of plastics and biomass exhibits a synergistic effect, significantly enhancing the yield and quality of bio-oil, biochar, and syngas. Integration of gasification and pyrolysis reduces activation energy, increases hydrogen production during co-gasification, and improves bio-oil calorific value. The gasification of polyethylene terephthalate with air in the presence of activated carbon limits tar formation with enhanced syngas production. Steam gasification enhances hydrogen generation by up to 40.0% compared to air gasification. Selective catalysts in the integrated pyrolysis–gasification process of biomass and plastics mixtures demonstrate optimisation of the production of high-purity carbon nanotubes and bio-oil. Application of innovative approaches such as microwaves, steam purging, and catalysts like zeolite or composite catalysts enhance heat transfer mechanism, tar cracking, and devolatilisation.
