Global gradients in intertidal species richness and functional groups
New publication by Jakob Thyrring and Lloyd Peck
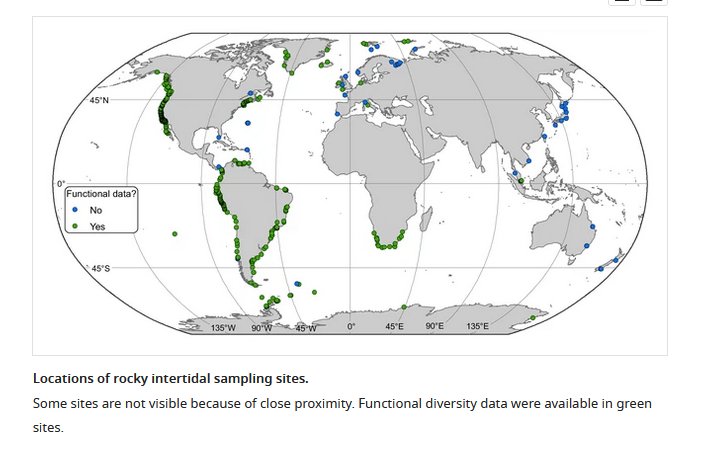
Abstract:
Whether global latitudinal diversity gradients exist in rocky intertidal a-diversity and across functional groups remains unknown. Using literature data from 433 intertidal sites, we investigated α-diversity patterns across 155° of latitude, and whether local-scale or global-scale structuring processes control α-diversity. We, furthermore, investigated how the relative composition of functional groups changes with latitude. α-diversity differed among hemispheres with a mid-latitudinal peak in the north, and a non-significant unimodal pattern in the south, but there was no support for a tropical-to-polar decrease in α-diversity. Although global-scale drivers had no discernible effect, the local-scale drivers significantly affected α-diversity, and our results reveal that latitudinal diversity gradients are outweighed by local-processes. In contrast to α-diversity patterns, three functional groups: predators, grazers and suspension-feeders diversity declined with latitude, coinciding with an inverse gradient in algae. Polar and tropical intertidal data were sparse, and more sampling is required to improve knowledge of marine biodiversity.
